Nutritional Content of Saltine Crackers: Saltine Crackers Nutrition Facts
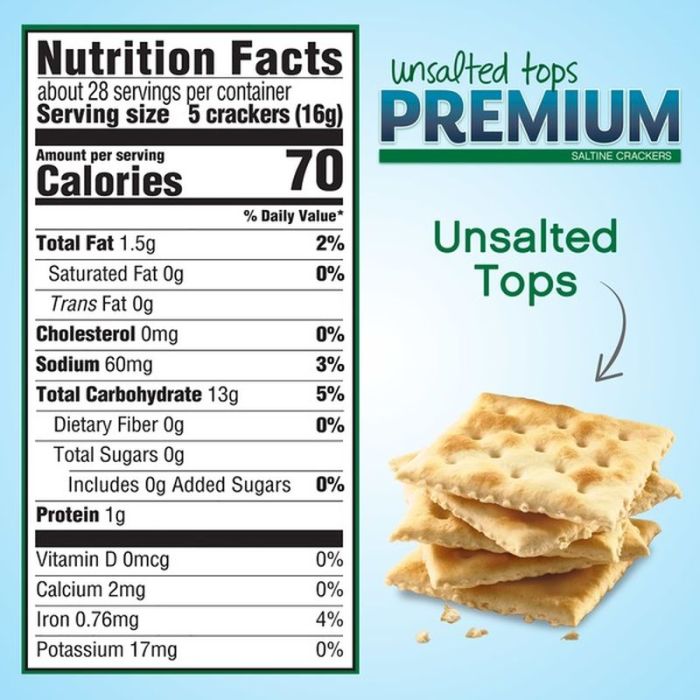
Saltine crackers nutrition facts – Saltine crackers, a staple in many pantries, offer a simple, often bland canvas for various culinary creations. However, understanding their nutritional profile is crucial for making informed dietary choices. This section details the macronutrient and micronutrient composition of a typical serving, providing a clearer picture of their place in a balanced diet.
Macronutrient Composition of Saltine Crackers
Saltine crackers primarily consist of carbohydrates, with a smaller contribution from protein and minimal fat. A typical serving (approximately 1 ounce or about 6 crackers) provides roughly 100-120 calories. The majority of these calories derive from carbohydrates, which are largely simple sugars and starches. Fiber content is relatively low, contributing only a small percentage to the total carbohydrate count.
Protein content is also modest, providing a minimal amount of this essential macronutrient. Fat content is generally low, mostly unsaturated fats, but can vary slightly depending on the brand and specific recipe. It’s important to note that these values can fluctuate slightly based on the manufacturer and specific product.
Micronutrient Composition of Saltine Crackers, Saltine crackers nutrition facts
While not a significant source of vitamins and minerals, saltine crackers do contain trace amounts of certain micronutrients. These typically include small quantities of iron, calcium, and some B vitamins. However, the amounts are generally insufficient to significantly contribute to daily recommended intakes. The fortification of saltine crackers with additional vitamins and minerals is not common practice.
Therefore, they should not be considered a primary source for these essential nutrients.
Comparison of Saltine Crackers to Other Cracker Types
The following table compares the nutritional profile of saltine crackers to that of wheat and rye crackers, highlighting differences in macronutrient and fiber content. Note that values are approximate and may vary depending on the specific brand and ingredients.
| Cracker Type | Calories (per serving) | Carbohydrates (g) | Fiber (g) | Protein (g) | Fat (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saltine Crackers | 110-120 | 20-25 | 1-2 | 2-3 | 1-2 |
| Wheat Crackers | 120-140 | 22-28 | 3-5 | 3-4 | 3-5 |
| Rye Crackers | 130-150 | 25-30 | 4-6 | 4-5 | 3-4 |
Sodium Content and Health Implications

Saltine crackers, while seemingly innocuous, contribute significantly to daily sodium intake. Understanding their sodium content and its potential health effects is crucial for maintaining a balanced diet and overall well-being. This section will examine the sodium levels in a typical serving of saltine crackers, compare them to recommended daily intakes, and discuss potential health risks associated with high sodium consumption, along with strategies for mitigating those risks.The sodium content in a typical serving of saltine crackers can vary depending on the brand and size of the serving.
However, a common serving size (approximately 12 crackers) often contains around 150-200 milligrams of sodium. This represents a considerable portion of the recommended daily sodium intake for many individuals.
Recommended Daily Sodium Intake and Saltine Cracker Consumption
The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends a daily sodium intake of no more than 2,300 milligrams (mg) for most adults, and ideally, an even lower limit of 1,500 mg for many individuals, particularly those with high blood pressure or other health concerns. Considering that a single serving of saltine crackers can contribute 150-200 mg of sodium, consuming multiple servings throughout the day can quickly push individuals closer to or even exceed their recommended daily limit.
This is especially relevant when considering that sodium is present in many other foods and beverages we consume. For example, a single serving of fast food or a processed lunch meat can easily contain several hundred milligrams of sodium.
Health Risks Associated with High Sodium Consumption
High sodium intake is strongly linked to several health problems. Excessive sodium consumption can lead to elevated blood pressure (hypertension), a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. The body retains excess fluid when sodium levels are high, increasing blood volume and consequently blood pressure. Over time, this chronic elevation of blood pressure damages blood vessels and organs.
Other potential health consequences associated with excessive sodium intake include increased risk of osteoporosis and stomach cancer.
Strategies for Mitigating Sodium Intake from Saltine Crackers
While completely eliminating saltine crackers from one’s diet may not be necessary for everyone, mindful consumption is key. Strategies for mitigating the risks associated with their sodium content include:
- Portion control: Sticking to a single serving size can significantly reduce sodium intake from saltine crackers.
- Choosing low-sodium options: Some brands offer reduced-sodium versions of saltine crackers. Comparing labels and opting for these can make a difference.
- Balancing sodium intake throughout the day: Be mindful of the overall sodium content of your diet. If you consume saltine crackers, reduce sodium intake from other sources such as processed foods, fast food, and salty snacks.
- Increasing potassium intake: Potassium helps balance the effects of sodium. Consuming potassium-rich foods like bananas, spinach, and sweet potatoes can help regulate blood pressure.
Comparison to Other Snack Foods
Saltine crackers, while seemingly innocuous, occupy a specific niche in the snack food landscape. Their nutritional profile, particularly their relatively low fat content and moderate carbohydrate levels, contrasts sharply with many popular alternatives. A comparative analysis reveals both advantages and disadvantages when choosing saltines over other common snacks.Saltine crackers offer a less calorically dense option compared to many processed snacks.
For instance, a serving of potato chips typically contains significantly more fat and calories than a similar serving of saltines. Similarly, pretzels, while lower in fat than potato chips, often contain higher levels of sodium. Fresh fruit, on the other hand, provides a superior nutritional profile with vitamins, minerals, and fiber, though it lacks the salty, crunchy satisfaction some find in crackers.
Nutritional Comparison of Snacks
The following table provides a simplified comparison of the nutritional content (per serving) of saltine crackers against pretzels, potato chips, and a serving of fresh fruit (e.g., an apple). Note that specific values can vary depending on brand and type. This table aims to highlight general trends rather than provide precise figures.
| Snack | Calories | Fat (g) | Sodium (mg) | Fiber (g) | Vitamins & Minerals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saltine Crackers (approx. 12 crackers) | 150-200 | 3-5 | 200-300 | 1-2 | Low |
| Pretzels (approx. 1 oz) | 100-150 | 1-3 | 200-400 | 1-2 | Low |
| Potato Chips (approx. 1 oz) | 150-200 | 10-15 | 150-250 | 0-1 | Low |
| Apple (medium) | 95 | 0 | 0 | 4 | High (Vitamins A & C, Potassium) |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Choosing Saltine Crackers
Saltine crackers present some advantages, particularly their lower fat content compared to potato chips. Their relatively lower calorie count can also be beneficial for weight management. However, their high sodium content is a significant disadvantage, posing potential risks for individuals with hypertension or sodium sensitivity. The limited nutritional value compared to fruits and vegetables is another drawback. They lack the significant amounts of vitamins, minerals, and fiber found in healthier alternatives.
Recommendations for Healthier Snack Choices
Instead of relying on saltine crackers, consider incorporating a wider variety of nutrient-rich snacks into your diet. Fruits, vegetables (like carrot sticks or bell pepper strips), nuts (in moderation), and yogurt offer superior nutritional benefits. Whole-grain crackers with added seeds or nuts can also be a healthier alternative, providing more fiber and nutrients. Prioritizing snacks that offer a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats contributes to better overall health and well-being.
For example, a small handful of almonds with an apple provides healthy fats, fiber, and vitamins. Air-popped popcorn, a whole-grain snack, is another lower-calorie and higher-fiber option compared to saltine crackers.
Saltine crackers, while convenient, are often low in essential nutrients. For a more balanced snack, consider adding toppings rich in vitamins and minerals; a good example would be a slice of red onion, whose nutritional profile you can explore further by checking out this helpful resource on red onion nutrition facts. Ultimately, understanding the nutritional content of both saltines and additions like red onions helps in making informed dietary choices.
Serving Size and Calorie Information
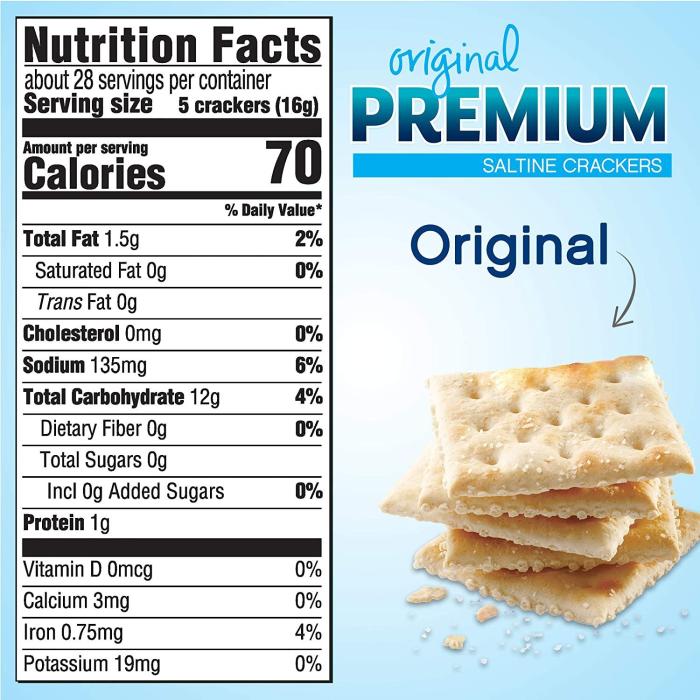
Understanding the serving size of saltine crackers is crucial for accurate calorie and nutrient tracking. A standard serving size is often defined by manufacturers and varies slightly depending on the brand and cracker type. However, a common reference point is a serving of approximately 12 crackers. This serving size will provide a baseline for understanding calorie and nutrient content.The calorie count for a standard serving (around 12 crackers) of saltine crackers typically falls within the range of 140-160 calories.
This can fluctuate slightly based on the specific brand, ingredients used, and any added flavors or seasonings. It’s essential to always check the nutrition label on the specific package for the most accurate calorie information.
Serving Size Variations and Calorie Intake
Variations in serving size directly impact the total calorie and nutrient intake. Consuming double the standard serving (approximately 24 crackers) would roughly double the calorie intake, resulting in approximately 280-320 calories. Similarly, consuming half a serving (around 6 crackers) would roughly halve the calorie intake, leading to approximately 70-80 calories. This principle applies to all nutrients present in the crackers; the amount consumed scales proportionally with the serving size.
For instance, sodium intake will also increase or decrease proportionally with the number of crackers consumed.
Visual Representation of a Standard Serving
Imagine a standard rectangular box of saltine crackers. A standard serving of 12 crackers could be visualized as a roughly rectangular stack of crackers approximately 1.5 inches wide, 2 inches long, and 0.5 inches high. This is an approximation, and the actual dimensions will vary slightly based on the size and shape of the individual crackers and how tightly they are stacked.
To further illustrate, one could picture a small, neat pile of crackers that would comfortably fit within the palm of an average-sized adult hand. This visual representation offers a practical understanding of the portion size.
Questions and Answers
Are saltine crackers gluten-free?
No, traditional saltine crackers contain wheat flour and are therefore not gluten-free.
Can saltine crackers be part of a weight-loss diet?
In moderation, yes. They are relatively low in calories compared to some snacks, but portion control is essential due to their carbohydrate content.
What are some healthier alternatives to saltine crackers?
Whole-grain crackers, rice cakes, or even fruits and vegetables offer more nutritional value and fiber.
Do saltine crackers contain any added sugars?
Most brands contain minimal added sugar, but it’s always best to check the ingredient list on the specific product you are consuming.
Are there low-sodium versions of saltine crackers available?
Yes, many brands offer low-sodium or reduced-sodium options.



